In the recent decade, medicine has experienced remarkable transformations in disease treatment, with personalized therapies emerging as pivotal agents of change. These therapies take into account each patient’s unique characteristics, leading to more effective disease management. The primary catalyst for this advancement stemmed from complex acquired illnesses such as cancer. A breakthrough was the development of chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), a revolutionary approach in cancer treatment1. As a result, 6 CAR-based medications are now approved for medical use2.
Autologous and allogeneic cell therapies are two distinct approaches to personalized cellular therapy, each with its own advantages:
- Autologous cell therapy involves using a patient’s own cells as the therapeutic agent. These cells are typically harvested from the patient, modified in the laboratory, and reinfused back into the same patient.
- Allogeneic cell therapy, on the other hand, involves using cells sourced from a donor other than the patient, typically selected on criteria such as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching and compatibility evaluation. However, one of the key challenges in allogeneic cell therapy is to overcome recipient immune rejection.
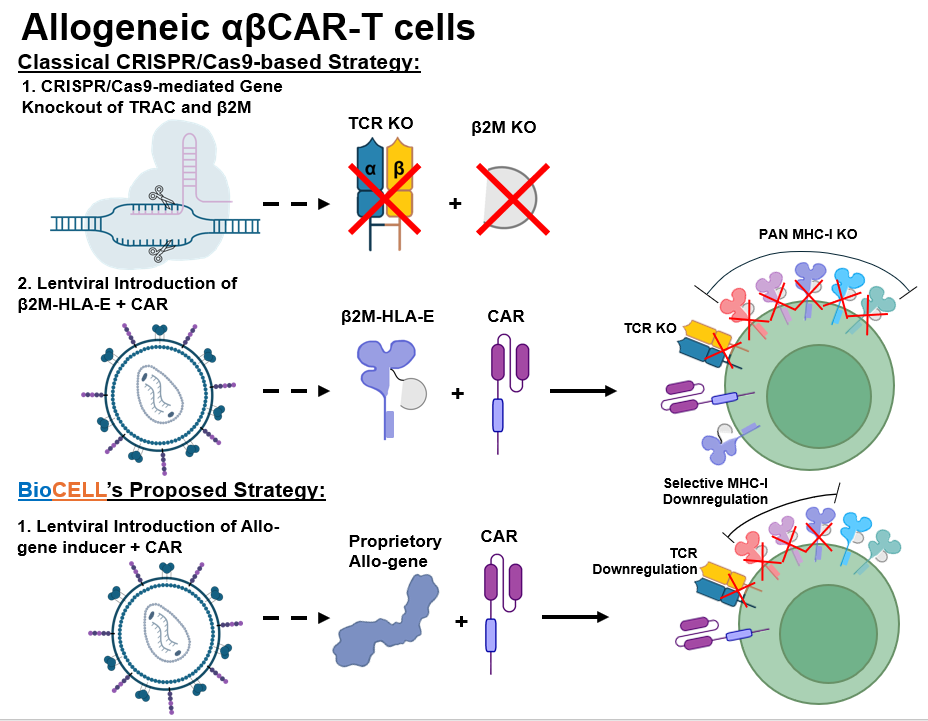
BioCELL’s innovative one-step process for generating potent allogeneic αβCAR-T cells addresses principal barriers such as preventing Graft vs Host Disease (GvHD) and increasing persistence in cancer immunotherapy. This streamlined approach developed with our collaborator, combines TCR and HLA modulation in a single step, powered by a proprietary allo-gene inducer. This novel allo-gene inducer ensures NK cell inhibition and improves CAR-T cell persistence. Moreover, the system’s modularity allows it to pair with any CAR in a single cassette, simplifying manufacturing and expanding therapeutic possibilities.
- Dabas, P., & Danda, A. (2023). Revolutionizing cancer treatment: a comprehensive review of CAR-T cell therapy. Medical Oncology, 40(9), 275.
- Chen, Y. J., Abila, B., & Mostafa Kamel, Y. (2023). CAR-T: what is next?. Cancers, 15(3), 663.

